User Scripts GUI¶
User Scripts can define their own configuration and allow the final user to modify it by providing a specialized GUI.
The GUI is defined into the User Script via the gui attribute:
local script = {
default_value = {
operator = "gt",
threshold = 50,
},
...
gui = {
i18n_title = "entity_thresholds.syn_victim_title",
i18n_description = "entity_thresholds.syn_victim_description",
input_builder = "threshold_cross",
}
...
}
The most important GUI attributes are:
i18n_title: (mandatory) a localization string for the title of the elementi18n_description: (mandatory) a localization string for the description of the elementinput_builder: defines the template which will be used to render the GUI. If it’s not defined, the user will only be able to enable or disable the user scripts without any additional configuration.
The default_value can be used to define a default for the configuration. Its format
depends on the input_builder used, see below for more information.
Input Builders¶
Input builders defines which template to use to render the GUI. The currently available input builders are:
threshold_cross: allow the user to define a threshold and an operator (“>” or “<”)items_list: allows the user to insert a list of itemslong_lived: template specialized for the long lived flows pluginelephant_flows: template specialized for the elephant flows pluginflow_mud: template specialized for the flow MUD plugin
Currently the user is limited to the above input builders but in the future it will be possible to define new input builders. The input builders backend code can be found in user_scripts_templates.lua whereas the frontend code can be found in scripts-list-utils.js.
Here is a description of the most useful input builders.
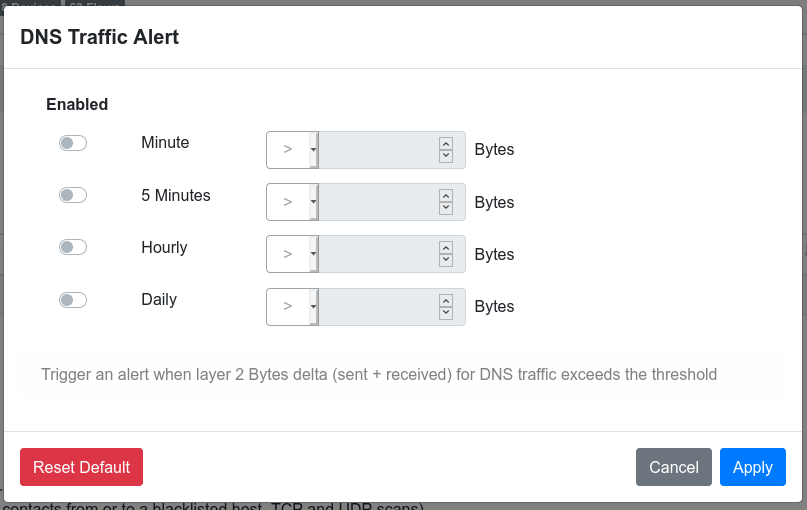
Threshold Cross¶
The Threshold Cross input builder allows the user to configure a threshold for a specific metric (e.g. the DNS traffic) for one or more granularities. Each granularity can be separately enabled.
When the threshold_cross input builder is used, the user script can specify some additional parameters into
the gui section:
field_max: max value for the threshold fieldfield_min: min value for the threshold fieldfield_step: step value for the threshold fieldfield_operator: can be used to fix a specific threshold operator:gtfor the “>” operator,ltfor the “<” operatori18n_field_unit: localization string to be displayed after the threshold field (e.g. “Bytes” in the example above). user_scripts.field_units provides some commonly used values.
Here is an example showing the usage of the threshold_cross input builder:
local script = {
...
gui = {
i18n_title = "entity_thresholds.syn_victim_title",
i18n_description = "entity_thresholds.syn_victim_description",
input_builder = "threshold_cross",
i18n_field_unit = user_scripts.field_units.syn_sec, -- Syn/Sec
field_max = 65535, -- Max 65535 Syn/Sec
field_min = 1, -- Min 1 Syn/Sec
field_operator = "gt"; -- Only ">" will be shown
}
}
function script.hooks.min(params)
local value = host.getSynFlood()["hits.syn_flood_victim"] or 0
-- Check if the configured threshold is crossed by the value and possibly trigger an alert.
alerts_api.checkThresholdAlert(params, alert_consts.alert_types.alert_tcp_syn_flood, value)
end
..
The current script configuration is available into params.user_script_config:
operator: containsgtfor “>” orltfor “<”threshold: contains the numeric value for the threshold
This information is internally used by alerts_api.checkThresholdAlert to check if the threshold is currently crossed and in such case trigger a threshold cross alert.
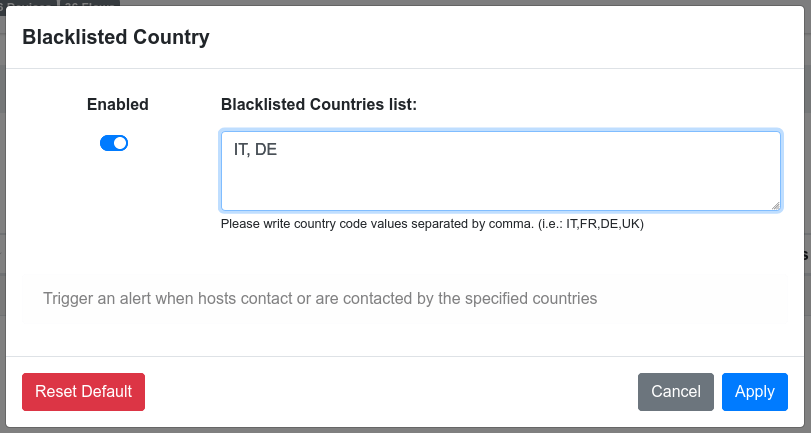
Items List¶
This input builder allows the user to insert a list of items. The items must be separated by a comma.
When using such input builder, the user
script must also specify the item_list_type: parameter into the
gui section, which tells ntopng the format of each item for the validation.
Here is a list supported types:
country: each item is a country code (e.g. “IT”)proto_or_category: each item is a protocol (e.g. Youtube) or category (e.g. SocialNetworks)string: each item is a single word (e.g. “www.ntop.org”)device_type: each item is a device type (e.g. “Printer”)
Here is an example showing the usage of the items_list input builder to check if flow is coming/going to one of the configured blacklisted countries:
local script = {
...
gui = {
i18n_title = "alerts_dashboard.blacklisted_country",
i18n_description = "alerts_dashboard.blacklisted_country_descr",
input_builder = "items_list",
item_list_type = "country",
}
...
}
function script.hooks.protocolDetected(now, conf)
local cli_country = flow.getClientCountry()
local srv_country = flow.getServerCountry()
-- conf.items contains the list of countries that the user has
-- configured from the GUI
for _, country in pairs(conf.items) do
if (country == cli_country) or (country == srv_country) then
print("Blacklisted country found! " .. country)
end
end
end
...
As shown into the example, the configured list of countries can be found
in conf.items.