ntopng was initially designed as a passive traffic monitoring tool. Over the years we have added active monitoring features such as network discovery, SNMP, and now vulnerability scan. A network vulnerability scanner is a tool designed to identify vulnerabilities (often know as CVEs) in network services such as a web or SSH server by performing an active service scan.
In ntopng we have decided to complement passive traffic with active scanning because:
- We want to identify vulnerabilities that can assist network and security administrators to implement a healthy network.
- Matching passive with active traffic analysis is something unique that only ntopng can features. Doing this we are able to identity:
- Active network services that are not in use and thus that can be safely shutdown.
- How critical are vulnerabilities: a highly vulnerable service with almost no traffic exchanged is less problematic than a popular service with less severe vulnerabilities.
- Hidden service, i.e. services for which we observe traffic but that are invisibile (i.e the port is closed) to scanner.
- Identify active hosts (with scanning) that o not send/receive meaningful traffic (i.e. traffic other than ARP, or multicast) and that (probably) represent unused assets. They need to be shutdown when possible as being them unused, and probably unmanaged, can create security issues to the whole network.
How to Use the Vulnerability Scanner
The ntopng vulnerability scan is designed to be open and modular, so that we can add overtime new components to the scanning engine. Currently it features the following modules:
- TCP and UDP portscan
- CVE and Vulners
To date all the above modules are based on nmap and for vulnerabilities on Vulscan: ntopng implements a GUI around the tools, matches scan output with ntopng traffic analysis, and deliver alerts using ntopng standard mechanisms.
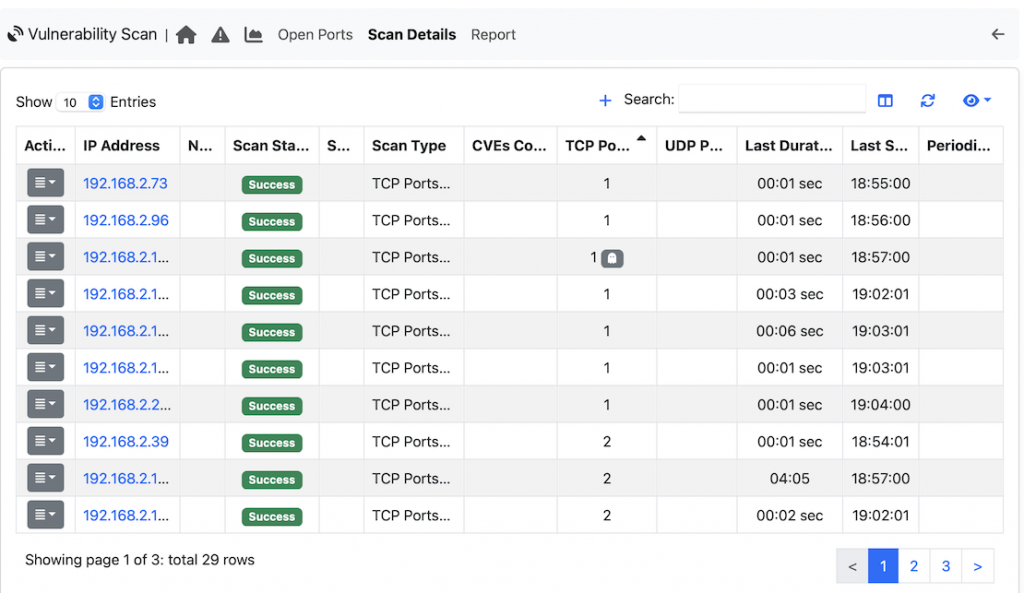
The Vulnerability Scan module can be accessed from the left sidebar under the Monitoring. The first step in add a host (or a set of hosts) that can be scanned: you can define the scan type, the ports to scan (all ports if the port field is empty, or the set of specified ports), the host or the network to scan, and the scan periodicity (one shot, or periodic ntopng-performed daily or weekly scan).
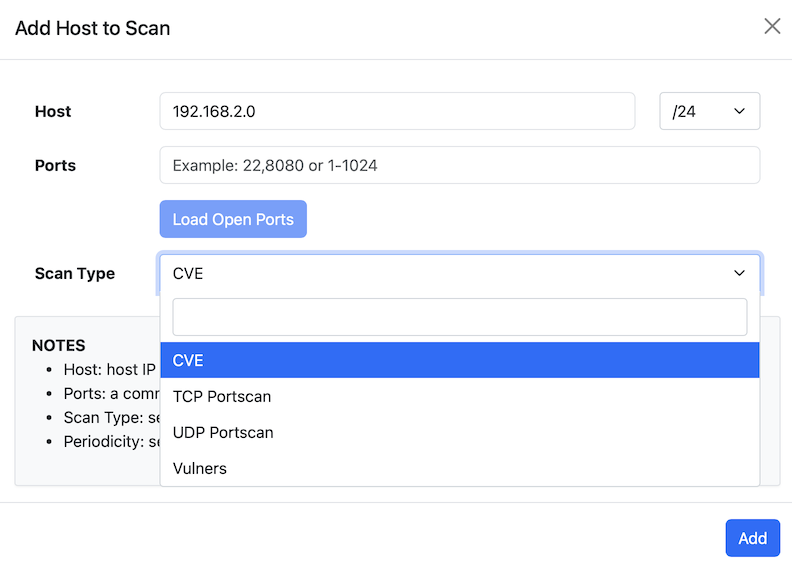
ntopng by default performs up to 4 concurrent scans that can be modified in preferences (minimum 1, maximum 16) according to user needs.
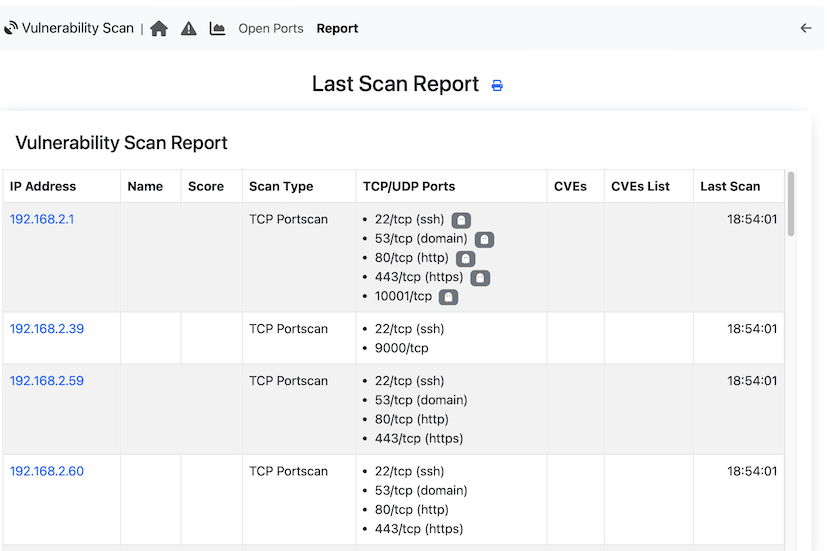
Clicking on the report page it is possible to have a summary of the scan result that can be printed or sent via email. Next to the port there is a ghost icon if the scanned port was not observed in ntopng monitored traffic.
In case of CVE scan, if found, they are listed according to their severity (reported in round brackets) that is a number up to 10,
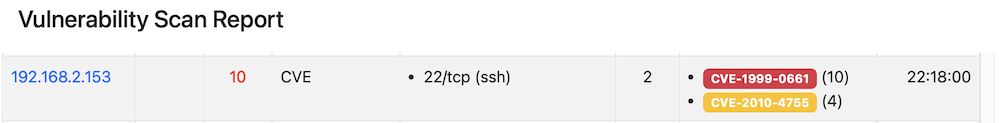
Clicking on the CVE badge, the page is redirected to the vulnerability database that describes in detail the CVE.
Future Work
In the future we plan to develop new scanning modules, for instance for the popular OpenVAS tool (a.k.a. Greenbone Community Edition). Another issue we would like to address is the false positive rate of the scanning modules as sometimes the engine reports CVEs that are not relevant for the scanned host.
Enjoy !
