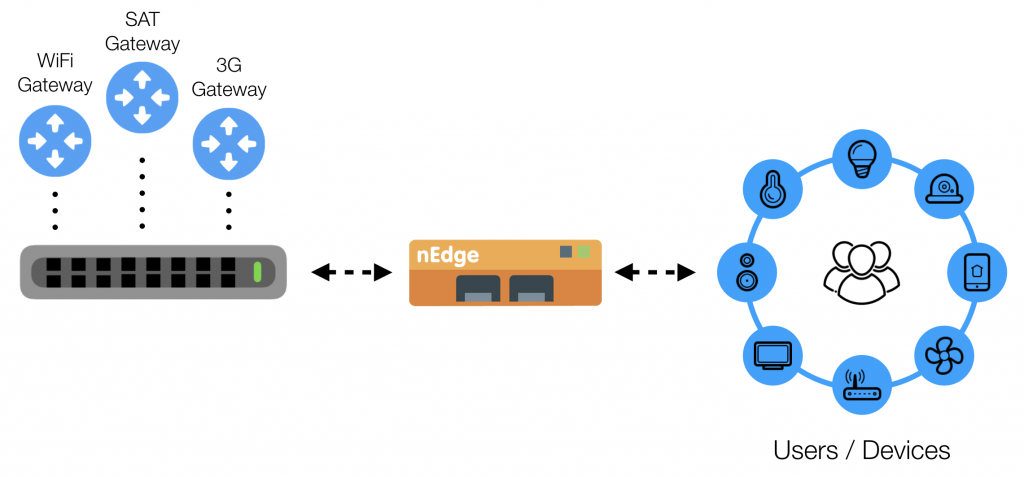
Exactly 3 years elapsed from the introduction of nEdge (ntopng Edge), and despite the fact we haven’t posted much about it in our blog, this tool continued to grow, many features have been added over time, and we see that every time new users have the chance to try it, they are amazed about the capabilities it provides.
If it’s the first time you hear about nEdge, we suggest to read the introductory post which explains how nEdge enables Network administrators to enforce policies at Layer-7 on network users, the nEdge product page which is providing a summary of the features, and the User’s Guide if you want to get the details of the implementation, deployment, and policies configuration.
In this post we want to update you about some of the latest features we added to nEdge in the past months, as a result of a few inquiries we received for easying the deployment in Networks with multiple (physical or virtual) LANs. In fact, although it was already possible to configure multiple WAN interfaces in nEdge, to handle dynamic Multi-Path Routing, it was not possible to configure multiple LAN interfaces to connect multiple internal Networks (e.g. the staff and the guest network).
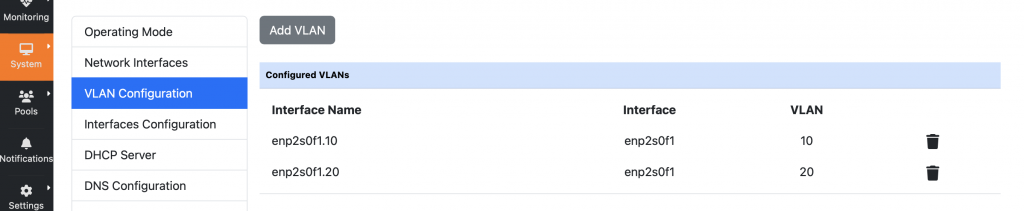
A releated feature that was also missing, is the ability to configure VLAN interfaces, which is also a key feature when handling multiple LANs (or WANs) as in most cases local network are virtualized and all traffic transits on a single link. Although it was possible to deploy nEdge as transparent bridge and enable the VLAN Trunk Bridging mode to handle traffic policing on a VLAN Trunk, it was not possible to configure and manage VLAN interfaces and treat them similar to physical interfaces when working in routing mode. This lets us save ports on the switch, and use a machine with only 2 ports for running nEdge.
Let’s see how all the above has been addressed in practice, and what are the steps to follow to configure and deploy nEdge in different network scenarios.
VLAN Configuration
As described in the Getting Started section of the User’s Guide, after installing and logging in the GUI for the first time, the system should be configured from the system interface, System -> System Setup page. Here it is possible to configure the Operating Mode (e.g. Routing) and select the Network Interfaces. At this point, after identifying the Network interfaces connected to our LAN or WAN Networks, it is possible to configure VLAN interfaces through the VLAN Configuration menu.
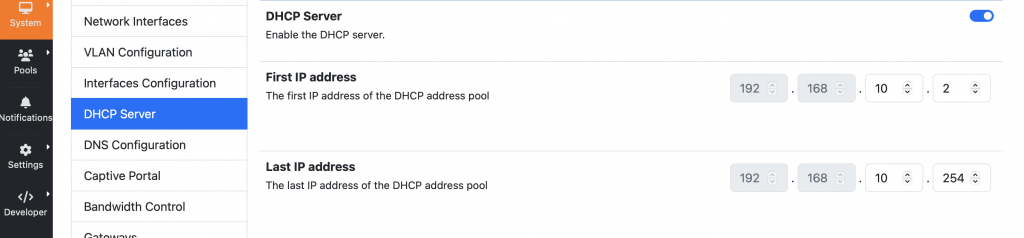
DHCP Service
nEdge provides the ability to configura a DHCP server for assigning IP addresses to the local Network. With the introduction of multiple LAN interfaces, we also added the ability to configure multiple DHCP servers to be able to assign IP addresses for all the different subnets. In order to do this, in the Interfaces Configuration section it is possible to assign the IP address to each LAN (or VLAN) interface, while in the DHCP Server section it is possible to select the IP address range and enable the service for each LAN (or VLAN) interface.
Multipath Routing
As described in the introduction, nEdge implements dynamic Multi-Path Routing, according to user-defined routing policies applied to the configured gateways. In most cases, a single WAN port is enough to route the traffic through one or more gateways, however this works in nEdge as long as all the gateways are on the same Network. If they are not on the same network, but you still want to use a single WAN port, it is now possible to use VLANs to configure one virtual Network interface for each gateway, and use them to configure routing policies.
Inter-LAN Filtering Rules
Having multiple local networks routed through nEdge introduces a new requirement, which is the ability to keep Network zones isolated, as they are usually used to segment the Network and control access to resources by means of Firewall policies. For this reason we introduced in nEdge the ability to define a Default Policy for Inter-LAN traffic, and define exceptions by means of filtering rules (e.g. accept traffic from Source IP A to Destination IP B or Local Network C). This can be configured from the System -> Inter-LAN Filtering Rules page.
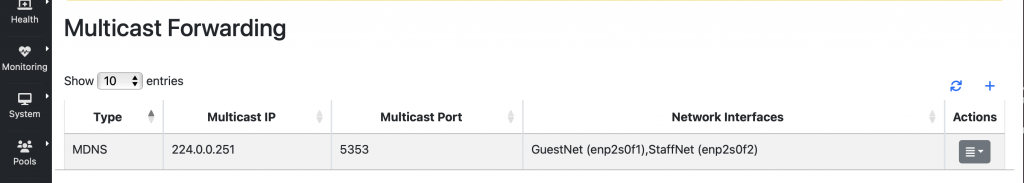
MDNS forwarding
One last feature we added in this context is the support for multicast traffic forwarding. Multicast traffic, used for instance by the mDNS service (used to resolves hostnames within local Networks with no need of a local name server), is not forwarded between local networks. In nEdge we added the ability to broadcast this traffic, forwarding selected multicast packets according to the defined policies, between LAN interfaces. This allows zero-conf devices to keep working also across subnets and can be configured from the System -> Multicast Forwarding page.
Have fun with nEdge!